With my dad’s recent heart attack and the likelihood that the nutritionist in rehab is pushing the conventional, outdated version of a “heart-healthy” diet, I wanted to take a deeper dive into what truly supports the heart, mind, and body. In our household, we’re already conscious of what we eat, but we don’t claim to know everything—this is a journey.
Just the other day, Neil was about to buy organic chips from Natural Grocers, but after checking the ingredients, we saw that every single one contained seed oils—so that was a hard no. That led to our next question: how can we make our own? Ideally, we’d love to find a way to participate in society without having to make everything from scratch, but until we get there, we’re learning how to navigate these choices with more confidence. So here’s some guidance we’ve gathered along the way to help you do the same.
For most of human history, our ancestors ate a diet naturally balanced in omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. But modern food systems have completely flipped the ratio, leaving most people overloaded with omega-6 while being dangerously deficient in omega-3. This imbalance fuels chronic inflammation, contributes to heart disease, and disrupts metabolic function. So, why is this happening, and what can we do to restore balance? Let’s dive into the omega-6 dilemma, how it affects our health, and how to correct it with smarter dietary choices.
What Are Omega-6 and Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Both omega-6 and omega-3 are essential fatty acids, meaning the body can’t produce them on its own—we must get them from food. They play crucial roles in brain function, inflammation regulation, and cardiovascular health. But here’s where things go wrong: they need to be in balance for optimal function.
Historically, humans consumed a roughly 1:1 to 4:1 ratio of omega-6 to omega-3, keeping inflammation under control. Today, however, most people eat a ratio closer to 20:1 or even 50:1, favoring omega-6—a drastic shift that drives systemic inflammation and chronic disease.
Why Are We Overloaded with Omega-6?
1. Industrial Seed Oils Are Everywhere
The biggest culprit in the omega-6 overload is the rise of industrial seed oils like:
- Canola oil
- Soybean oil
- Corn oil
- Cottonseed oil
- Safflower oil
- Sunflower oil
These oils are cheap to produce, highly processed, and used in nearly all packaged and restaurant foods. They dominate grocery store shelves and food supply chains, replacing traditional fats like butter, tallow, and coconut oil.
2. Processed and Fast Foods Are Loaded with Omega-6
Most processed foods—from chips and salad dressings to baked goods and frozen meals—contain high amounts of omega-6 due to seed oils. Even seemingly healthy options like store-bought hummus, nut butters, and protein bars often use these inflammatory oils.
3. Factory-Farmed Meat and Eggs Contain More Omega-6
Traditional pastured meats and wild-caught fish are naturally high in omega-3. But today, most livestock is grain-fed, consuming corn and soy, which shifts the fat profile of their meat, making it higher in omega-6 and lower in omega-3. Factory-farmed eggs, pork, and chicken are particularly affected.
4. Modern Diets Lack Omega-3-Rich Foods
At the same time that omega-6 intake has skyrocketed, most people aren’t eating enough omega-3-rich foods like:
- Wild-caught fatty fish (salmon, sardines, mackerel)
- Pastured eggs
- Grass-fed meats
- Walnuts
- Flaxseeds while omega-3 rich are also super high in phytoestrogens so I don’t recommend them
- Chia seeds in small quantities because they do contain low amounts of phytoestrogens
The result? A widespread imbalance in the omega-6 to omega-3 ratio, setting the stage for chronic inflammation.
How an Omega-6 Overload Affects Your Health
While omega-6 isn’t inherently bad, too much of it—without enough omega-3 to balance it—causes problems. Here’s how an omega-6-heavy diet impacts the body:
Chronic Inflammation
Omega-6 fats are precursors to pro-inflammatory molecules (prostaglandins and leukotrienes). While inflammation is a necessary immune response, excess omega-6 drives low-grade, chronic inflammation, linked to:
- Heart disease
- Arthritis
- Autoimmune disorders
- Obesity
- Neurodegenerative diseases
Increased Risk of Heart Disease
While mainstream nutrition still pushes polyunsaturated fats as “heart-healthy,” newer research shows that an excess of omega-6 promotes arterial inflammation and oxidative stress, increasing heart disease risk.
Metabolic Dysfunction and Weight Gain
Studies suggest that excessive omega-6 intake contributes to insulin resistance and obesity. Since omega-6 fats accumulate in cell membranes, they can disrupt metabolic signaling, making the body less efficient at burning fat.
Cognitive Decline and Mental Health Issues
Omega-3s, especially DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are critical for brain function. A high omega-6 to omega-3 ratio has been linked to:
- Higher rates of depression and anxiety
- Increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease
- Brain fog and difficulty concentrating
How to Restore the Omega-6 to Omega-3 Balance
The good news? You don’t need to eliminate omega-6 entirely—you just need to cut back on excessive sources and increase omega-3 intake to restore balance.
1. Ditch Industrial Seed Oils
The most impactful step is removing processed seed oils from your diet. Instead, choose healthy, traditional fats like:
- Grass-fed butter and ghee
- Coconut oil
- Extra virgin olive oil
- Pastured animal fats (tallow, lard)
- Cold-pressed avocado oil
2. Avoid Processed and Restaurant Foods
Since most packaged and restaurant foods contain hidden seed oils, cooking at home with real ingredients is key. Read labels carefully—even organic and “healthy” brands sneak in omega-6-heavy oils.
3. Choose Grass-Fed and Pasture-Raised Animal Products
Opt for grass-fed beef, pastured eggs, and wild-caught seafood whenever possible. These foods naturally contain higher omega-3 levels and lower omega-6 compared to their conventional counterparts.
4. Eat More Omega-3-Rich Foods
To help correct the imbalance, prioritize foods rich in omega-3s.
Animal-Based Sources (Highest in EPA & DHA, the Most Bioavailable Forms of Omega-3s)
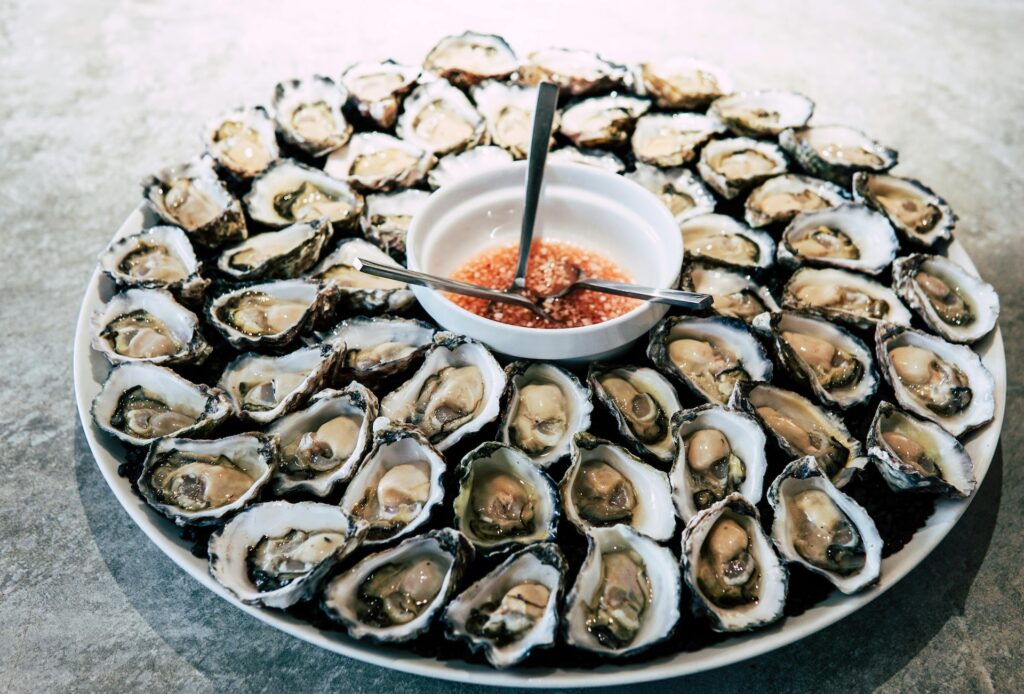
- Wild-caught salmon, sardines, mackerel – Among the best sources of omega-3s (EPA & DHA)
- Anchovies – Small but packed with omega-3s and low in mercury
- Herring – A traditional omega-3-rich fish that’s often fermented or smoked
- Trout (wild-caught) – High in omega-3s and lower in contaminants than farmed fish
- Grass-fed beef and dairy – Higher in omega-3s than grain-fed counterparts
- Pastured eggs – Contain more omega-3s than conventionally raised eggs
- Cod liver oil – A concentrated source of omega-3s, plus vitamin A & D
- Mussels and oysters – High in omega-3s, plus zinc and B12 for overall health
Plant-Based Sources (ALA, Which the Body Converts to EPA & DHA Less Efficiently)
- Walnuts – One of the best plant-based omega-3 sources
- Seaweed and algae – Some of the best plant-based sources of DHA, ideal for vegans
- Spirulina and chlorella – Algae-based superfoods containing omega-3s and other nutrients
- Chia seeds – High in ALA-rich source with added fiber benefits, but does contain a low amount of phytoestrogens
- Hemp seeds – Lower in omega-3s than chia and some phytoestrogens, but also less than chia seeds
- Perilla seeds – High in ALA, often used in Asian cuisine, but do contain low amounts of phytoestrogens
5. Consider Omega-3 Supplements
If getting enough omega-3s from food is challenging, consider taking a high-quality fish oil or cod liver oil supplement with EPA and DHA to help bring your ratio back into balance.
TL;DR
Most people today consume far too much omega-6 while being severely deficient in omega-3. This imbalance fuels chronic inflammation, heart disease, and metabolic dysfunction—but by making intentional food choices, we can restore the balance our ancestors enjoyed.
The key? Ditch industrial seed oils, avoid processed foods, prioritize pastured meats and wild-caught fish, and increase omega-3-rich foods. Small changes can have a huge impact on long-term health and inflammation levels.
For more insights on ancestral nutrition and holistic health, explore more at Mother Luck Ranch!
Disclaimer
According to the FDA, only medical professionals can give medical advice. Neither Julie nor Neil are “medical professionals” or “qualified health providers.” We believe in educating ourselves and our community on holistic alternatives to allopathic medicine. As such, the FDA legally restricts the language we can use as citizens and business owners in the United States of America.
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article. The use of any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.